Gout Definition
Gout is a disorder in which deposits of uric acid crystals build up in the joints as a result of high concentrations of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricaemia). The crystal accumulations cause flare-ups (crises) of painful inflammation in and around the joints.
The build-up of uric acid crystals can intermittently cause severe pain and inflammation in joints or tissues.
Gout Management
Drugs are given to relieve the inflammation and pain caused by flare-ups, and different drugs (usually taken for life) are used to lower blood concentrations of uric acid which, over time, reduce uric acid deposits and prevent recurrence of flare-ups.
Gout is more common in men than in women. It usually occurs in middle-aged men and post-menopausal women. It is rare in young people, but is usually more severe in those who have developed the disease before the age of 30. Gout, caused by high levels of uric acid (hyperuricaemia), often runs in families.
Here a great community that share all about natural medicine for gout: Gout Home Remedy.
Blood levels of uric acid tend to be high in people with metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is characterised by a large waistline (due to excess abdominal fat), high blood pressure, resistance to the effects of insulin (called insulin resistance) or high blood sugar levels, as well as abnormal concentrations of cholesterol and other blood lipids.
Coronary artery disease and metabolic syndrome are common among people with gout.
Gout Causes
Uric acid, which is a by-product of the breakdown of nucleic acids (ribonucleic acid [RNA] and deoxyribonucleic acid [DNA]) in cells. It is present in small amounts in the blood, because the body continually breaks down cells and forms new cells. In addition, the body easily converts certain substances in food, called purines, into uric acid. Purines are building blocks of RNA and DNA. Uric acid is removed from the blood mainly through the kidneys and the gastrointestinal tract.
Abnormally elevated uric acid levels in the blood are the result of:
- Decreased uric acid elimination by the kidneys (the most common cause) or the gastrointestinal tract
- excessive consumption of purine-rich foods and/or alcohol (usually a minor factor)
- production of excess uric acid (rare)
Often, the concentration of uric acid in the blood becomes unusually high when the kidneys cannot sufficiently eliminate it through the urine. This cause is usually determined by the subject’s genes. An excess of uric acid in the blood can lead to the formation and deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints. Conditions that can affect the kidneys’ ability to remove uric acid also include:
- Some types of kidney disease
- Certain drugs
- saturnism (lead poisoning)
Excessive consumption of purine-rich foods (liver, kidneys, anchovies, asparagus, consommés, herring, meat sauces and soups, mushrooms, mussels, sardines and sweetbreads) can increase the level of uric acid in the blood. However, a strict low-purine diet reduces the uric acid level by only a small amount. In the past, when meat and fish were scarce, gout was considered a disease of the rich.
Combining high-purine diets with alcohol or especially drinks containing high fructose corn syrup can make problems worse, because all these drinks can increase uric acid production and make it more difficult to be eliminated through the kidneys.
For unknown reasons, not all people with an abnormally high concentration of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricaemia) develop gout. Therefore, gout should not be diagnosed by blood test alone.
Risk factors for the development of gout
- Beer (including non-alcoholic beer) and spirits
- Foods and beverages containing high fructose corn syrup
- Certain foods (especially anchovies, asparagus, consommé, herring, meat sauces and broths, mushrooms, mussels, all offal, sardines and sweetbreads; red meat, poultry and fish contribute in part to elevated uric acid concentrations)
- Low daily intake of dairy products
- Certain cancers and blood diseases (such as lymphoma, leukaemia and haemolytic anaemia)
certain medications (such as thiazide diuretics, cyclosporine, pyrazinamide, ethambutol and nicotinic acid) - Saturnism (lead poisoning)
- Obesity
- Psoriasis
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Chronic kidney disease
- Some rare enzyme disorders
- Starvation
Did you know that?
In the past, when meat and fish (purine-rich foods) were scarce and the rich feasted on wine and beer, gout was considered a disease associated with wealth.
High levels of uric acid in the blood often lead to high levels of uric acid in the joints. This process results in the formation of uric acid crystals in joint tissue and intra-articular fluid (synovial fluid).
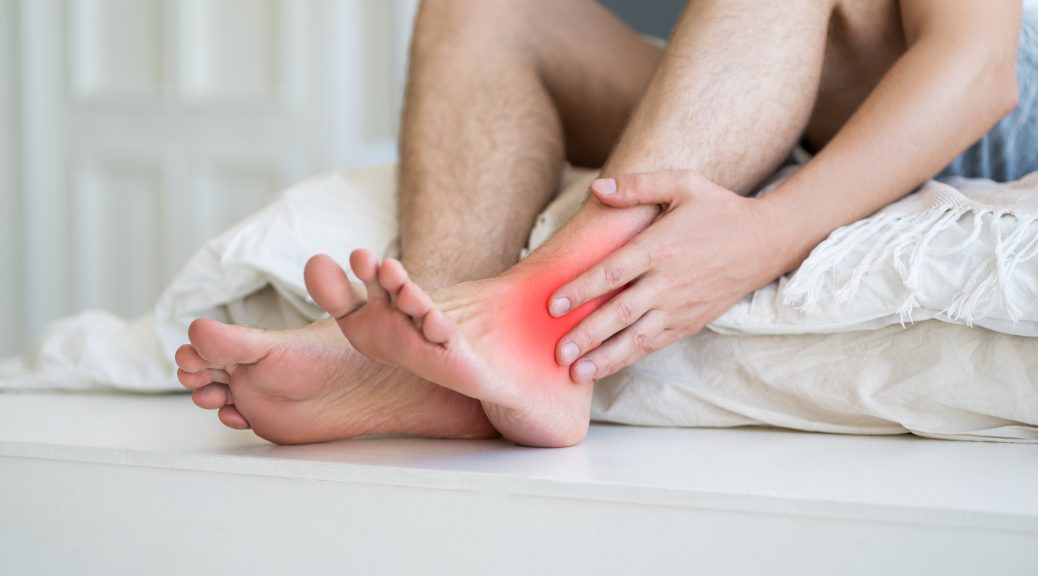
Gout most commonly affects the joints of the foot, especially the base of the big toe (the swelling, pain and redness of the big toe is called podagra). However, other areas are also frequently affected: the ankle, instep, knee, wrist and elbow. Gout tends to affect colder areas of the body because uric acid crystals form more easily there than in warmer areas. Rarely, gout affects joints in the warmer, central area of the body, such as those of the spine, hips or shoulders.
Sudden, severe flare-ups of gout (acute gouty arthritis) can occur without warning. They can be triggered by
- Injury
- Illness (such as pneumonia or other infection)
- Surgery
- Initiation of treatment with certain medications (such as diuretics, allopurinol, febuxostat, probenecid, and nitroglycerin, particularly intravenous nitroglycerin, which contains alcohol) that can abruptly change uric acid levels in the blood (but often these medications are medically necessary)
- Consumption of large amounts of alcohol or purine-rich foods
Gout Symptoms
Typically, during a flare-up, severe pain occurs suddenly in one or more joints, often at night. The nocturnal pain probably occurs because fluid that has accumulated in the joint during the day leaves the joint more quickly than uric acid when the subject is lying down, causing the uric acid to concentrate and thus form crystals more easily. The pain gets progressively worse and often becomes unbearable, especially when moving or touching the joint.
The joint becomes inflamed, swollen and warm, and the skin over it becomes reddish or purplish, tight and shiny.
Other symptoms of a flare-up are sometimes
- Fever
- Acceleration of the heart rate (tachycardia)
- A feeling of general malaise
- Chills (very rarely)
The first outbreaks usually affect only one joint and last at most one week.
Symptoms gradually disappear, joint function is restored and no symptoms reappear until the next flare-up. However, if the disease progresses, untreated flare-ups last longer, occur more frequently and affect several joints. Without treatment, subsequent outbreaks can last up to 3 weeks. A person with an outbreak who develops a fever above 101° F (38.3° C), chills, or any other severe symptoms (e.g., weakness, vomiting, rash, or any difficulty breathing), especially if there is no experience with previous outbreaks or if this is the first outbreak, should call a doctor or go to an emergency department, as these symptoms may also be due to a joint infection or a completely different problem.
After repeated outbreaks, gout can become severe and chronic and can lead to joint deformity.
Over time, joint mobility becomes progressively restricted as a result of damage caused by uric acid crystal deposits in the joints and tendons.
Read here to know if you have gout: Gout Symptoms.
==> You have the solution with this natural home remedy made of Boswellia and Curcuma in cream form: Gout Cure.